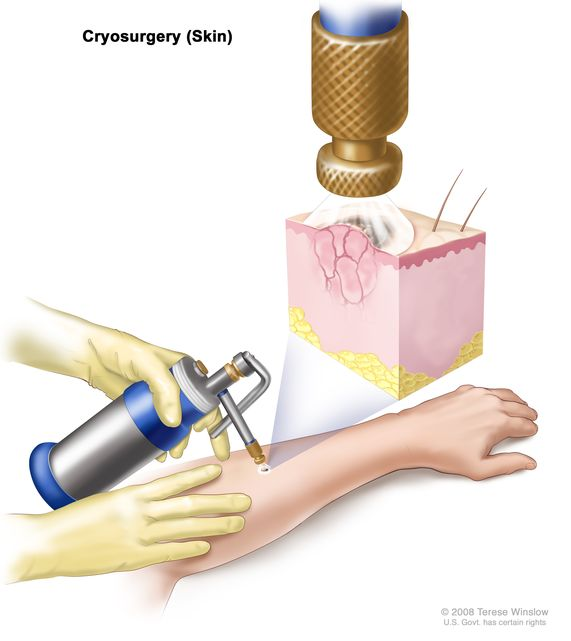
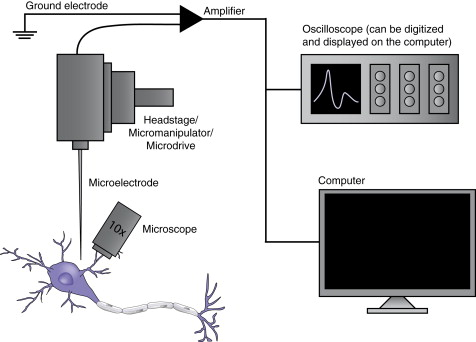
Anjali Singh
Anjali Singh is a freelance writer. Following her passion for science and research, she did her Master’s in Plant Biology and Biotechnology from the University of Hyderabad, India. She has a strong research background in Plant Sciences with expertise in Molecular techniques, Tissue culture, and Biochemical Assays. In her free time outside work, she likes to read fictional books, sketch, or write poems. In the future, she aspires to pursue a doctorate in Cancer Biology while continuing her excellence as a scientific writer.