Neuwirth Hole Board Test™
A unique water maze designed to study spatial navigation strategies, including allocentric and egocentric orientation systems, with applications in aging and cognitive research.
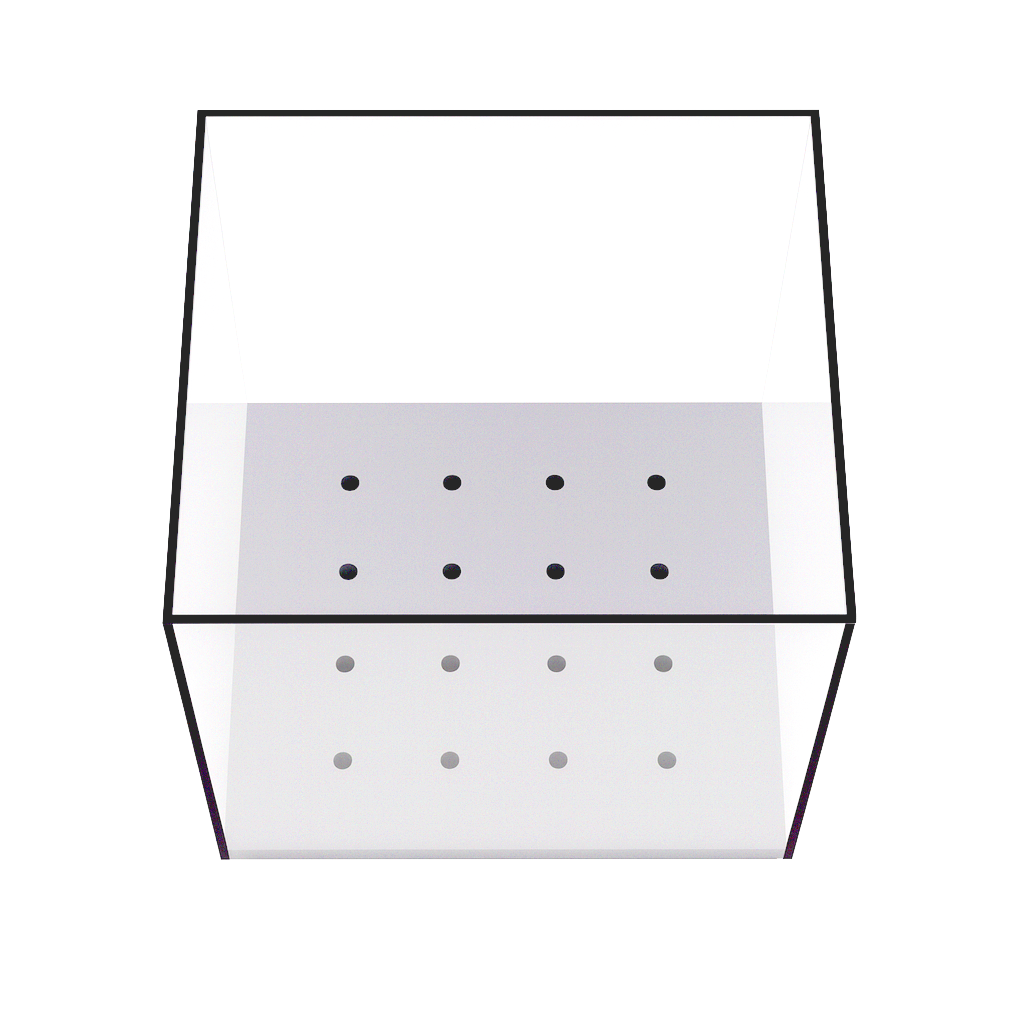
Overview
The Neuwirth Hole Board Test™ expands on the conventional rodent Hole Board test to study both anxiety-like behaviors and exploratory behaviors across different ages, strains, and sexes of rodents.
By incorporating spatial odor discrimination cues, this apparatus enables researchers to assess exploratory drive, learning, and memory in addition to fear and escape responses. The test runs over a two-day protocol:
Day 1 – measures anxiety-like behaviors in a novel environment (freezing, head poke latency, frequency).
Day 2 – introduces olfactory cues at the corners, encouraging exploration and allowing measurement of inhibitory shift (avoidance → approach behaviors).
This dual capability makes the Neuwirth Hole Board Test™ a versatile tool for cognitive and behavioral neuroscience research.
Market Opportunity
Traditional Hole Board tests often conflate exploratory drive with anxiety behaviors. The Neuwirth adaptation offers:
Clearer separation of anxiety vs. exploration over a two-day paradigm.
Ability to detect developmental, sex, and strain-specific differences.
Expanded applications in pharmacology, neurodevelopmental disorders, and neurotoxicology.
Compatibility with disease models where GABAergic dysfunction, anxiety, or cognitive deficits are expected.
spectrum disorders, schizophrenia, and age-related cognitive decline.
Offering flexibility for both academic research and translational neuroscience applications.
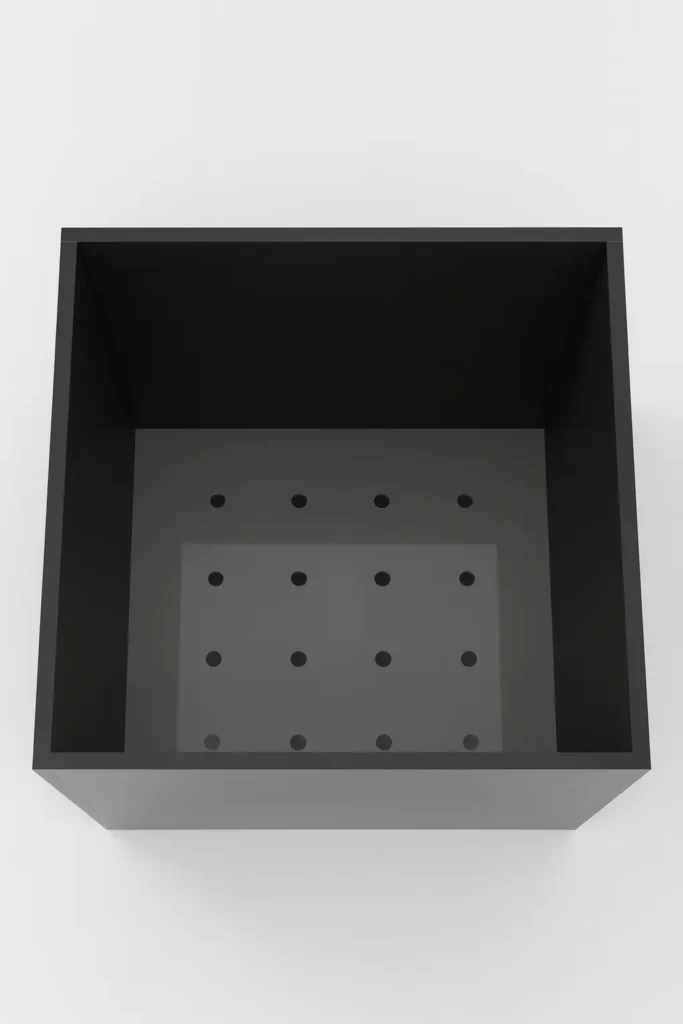
Invention & Advantages
Dual-day protocol
First day for anxiety/fear, second day for exploratory behaviors.
Odor discrimination
Incorporates contextual odor cues for spatial learning.
Flexible floor inserts
Multiple floor types (hole sizes for different developmental stages).

Cognitive range
Tests learning, memory, habituation, risk assessment, and arousal.
Pharmacological and disease modeling
Sensitive to drug manipulations, brain lesions, and neurodevelopmental models.

Easy maintenance
Odor-free design, simple cleaning with 70% ethanol.
Applications
Behavioral Parameters
Time spent mobile vs. freezing (Day 1 and Day 2).
Latency to first head poke.
Number and total time of head pokes.
Shifts in behavior across days (anxiety → exploration).
Use Cases
Study of exploratory drive, anxiety-like behavior, and inhibitory control.
Evaluation of pharmacological interventions.
Developmental and strain-specific behavioral comparisons.
Assessment of GABAergic system functions.
Principal Investigator
Professor Lorenz Neuwirth
References
Neuwirth, L. S., Volpe, N. P., Corwin, C., Ng, S., Madan, N., Ferraro, A. M., Furman, Y., & El Idrissi, A. (2017). Taurine Recovery of Learning Deficits Induced by Developmental Pb2+ Exposure. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 975 Pt 1, 39–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024-1079-2_4
Apparatus & Equipment
Mouse Neuwirth Hole Board™ – $3,290
- Dimensions: 25 × 25 × 25 cm
- Hole diameter: 2 cm
- Includes removable hole insert
Rat Neuwirth Hole Board™ – $3,690
- Dimensions: 50 × 50 × 50 cm
- Hole diameter: 2.54 cm
- Includes removable hole insert
Training Protocol
- Day 1 – Anxiety Behavior
Place rodent in apparatus for 10 minutes.
Record freezing, mobility, latency to first head poke.
- Day 2 – Exploratory Behavior
Place Petri dishes with four different odorants under each corner.
Record exploratory measures as on Day 1.
Compare shifts in anxiety vs. exploration.
Strengths & Limitations
Strengths
- Separates exploratory vs. anxiety measures.
- Tests a broad range of unconditioned behaviors.
- Supports pharmacological, developmental, and disease model studies.
Limitations
- Requires rigorous cleaning to avoid odor contamination.
- Exploration is essential—lack of it may confound anxiety measurement.
- Age, sex, and strain influence results.
- Susceptible to unintended environmental stimuli.

Interested in bringing your innovation to life?
If you’re an inventor or would like more information on any of the mazes, we’d love to hear from you
