
Model | Capacity | Duration | Pumping Rate(μL/hr) | Flow Regulator* Cap |
|---|---|---|---|---|
RWD-1003D | 100μl | 3D | 1 | Without |
RWD-1001W | 100μl | 1W | 0.5 | Without |
RWD-1002W | 100μl | 2W | 0.25 | Without |
RWD-1004W | 100μl | 4W | 0.125 | Without |
RWD-1006W | 100μl | 6W | 0.083 | Without |
RWD-2003D | 200μl | 3D | 2 | PE material |
RWD-2001W | 200μl | 1W | 1 | PE material |
RWD-2002W | 200μl | 2W | 0.5 | PE material |
RWD-2004W | 200μl | 4W | 0.25 | PE material |
RWD-2ml1W | 2ml | 1W | 10 | PE material |
RWD-2mL2W | 2ml | 2W | 5 | PE material |
RWD-2ml4W | 2ml | 4W | 2 | PE material |
*Flow regulator_Tube: 304 stainless steel material. Infusion_Syringe:Flat head for the injection of liquid.
The implantable osmotic release pump is an inexpensive cutting-edge drug delivery system. You can use this small implantable infusion pump for preclinical pharmaceutical research in mice, rats, and other laboratory animals. The mini-pump delivers drugs, hormones, and other test compounds at continuous and controlled rates, for terms extending from one day to a month and a half, without the requirement for external interference. The implantable pumps utilize osmosis for continuous infusion of unrestrained laboratory animals.
In the previous three decades, drug delivery research has made critical headways because of the recent developments and innovations in the fields of pharmaceutical sciences including pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and biopharmaceutics. Low development costs and regulated drug delivery pushed the research. Hence a significant portion of the novel drug delivery frameworks is upgraded such that the drug dose and dosing interim are reduced thereby maintaining optimum therapeutic dose and efficacy. These innovative drug delivery systems have been designed to regulate drug release over an extended time frame. Furthermore, recent advances have been made to make the rate and extent of the drug release independent of physicochemical properties of drugs and excipients, and physiological factors like pH of the gastrointestinal tract, the presence of food, and nutritional health.
Osmotic pumps are the most promising procedure based systems for controlled drug delivery. The controlled drug delivery system is mediated by osmosis which can be characterized as the net movement of water molecules over a selectively permeable film driven by a difference in osmotic gradient over the layer. The difference in solute concentration over the membrane permits entry of water, however, rejects most solute particles. Osmogens create osmotic pressure to stimulate drug release from the pump.
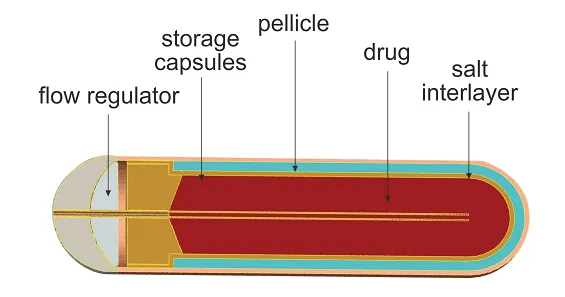
In cross-section, the implantable osmotic release pumps are composed of a drug core (reservoir), the diffusion agent, and the tissue layer (rate controller). Additionally, a flow moderator is inserted into the body of the diffusion pump. It is a kind of an implantable system within which you can load a solution or suspension contained in a cylindrical reservoir shaped from an artificial collapsible, impervious stuff wall (e.g., polyester) that is open to the external surroundings via a single orifice.
The main components of an implantable osmotic release pump include the drug compound (water-soluble or insoluble), osmotic agents (ionic compounds of inorganic salts), a stable semi-permeable membrane, plasticizers, flux regulators, wicking agents, pore forming agent, and coating solvent.
Our implantable osmotic release pump is available in three different sizes to offer the researchers a variety of dosing capacities, release rates, and duration. You can load it with 100 µl, 200 µl, and 2 ml of the test compound.
The implantable osmotic pump employs an osmotic gradient inside the lumen called the salt sleeve and the tissue condition in which the pump is implanted. The high osmolality of the salt sleeve makes water flow into the pump through a semipermeable film which encases the external surface of the pump. As the water enters the salt sleeve, it compresses the flexible reservoir, dislodging the test substance from the tube at a controlled rate. The rate of drug delivery is directly proportional to the osmotic pressure of the core. Since the delivery system cannot be refilled, these pumps are intended for single use only.
The rate of the drug delivery by our osmotic pump is controlled by the water penetrability from the pump’s external film. In this manner, the drug delivery is independent of the drug formulation and excipients. Drugs of different atomic arrangements, including ionized medications and macromolecules, can be administered persistently at controlled rates. The sub-atomic weight of a compound, or its physical and chemical properties, does not affect the rate of the drug delivery by the implantable osmotic release pumps.
The osmotic pumps can be implanted subcutaneously or intraperitoneally depending on the size of the animal. For targeted drug delivery, a catheter can be attached to the osmotic pump to gain access to the tissues of interest. Subcutaneous implantation is technically the easiest and least intrusive procedure. Follow these steps for subcutaneous implantation:
The osmotic system can also be implanted in the peritoneal cavity of the larger animals. Follow the below-mentioned protocol for intraperitoneal injection:
Keep in mind that the pumps should be explanted if the animals survive after active infusion. The pumps must be removed no later than the first half-life of the test compound. The pump should be removed to measure the residual volume to confirm delivery, verify a drug’s stability, and assure the bioactivity of the test compound.
Implantable consistent infusion osmotic pumps have many applications in preclinical drug delivery improvement. The system empowers continuous and controlled dosing permitting the accomplishment of enduring state conditions and precise drug delivery. The system offers the researchers temporal and spatial control over the drug release. It circumvents poor-availability hurdles in the challenging therapeutic studies of hormones and growth factors. Also, the drugs with faster clearance rates and shorter half-lives require a consistent dosage that can be easily achieved by the implantable osmotic release pumps. Furthermore, it can assist the drug delivery of the compounds having a lower therapeutic index by continuous infusion while avoiding toxic concentrations. Moreover, the osmotic systems not only deliver the drugs with moderate solubility but also with extreme solubility.
Continuous infusion of the therapeutic compounds with the help of the implantable osmotic release pump assists the experimenters to establish parameters of the drugs with unknown pharmacokinetics. These pumps can also be used for a comparative study of the efficacy of different drugs administered through different routes. In addition to the drug efficacy analysis, these drug delivery systems can also be used for the targeted delivery of chemotherapeutic agents to the tumors with the help of an attached catheter. The osmotic release pumps can not only be used for chemotherapeutic preclinical studies but also to monitor cell proliferation to assess the carcinogenic potential of the cells. Also, these pumps improve bio-luminescence imaging studies by continuously delivering bio-luminescent substrates.
Applications of the osmotic release pump include the disciplines of oncology, stem cell research, gene transfection, gene silencing, neuroscience research, and preclinical pharmacological studies.
Osmotic pumps are one of the novel pharmaceutical tools for controlled and consistent drug delivery. Osmotic drug delivery pumps commonly comprise a drug center containing osmogen that is covered with a semipermeable layer. This covering has at least one transportation ports through which the test compound or suspension of the medication is discharged after some time. Different endeavors are underway to make an effective osmotic drug delivery system like pulsatile delivery with an expandable hole, and a lipid osmotic pump containing a smaller capsules than the usual osmotic pump for continuous and extended-release.
No questions yet for this product.
