Rondi Reig Star Maze
Advancing rodent behavioral research through spatial odor discrimination.
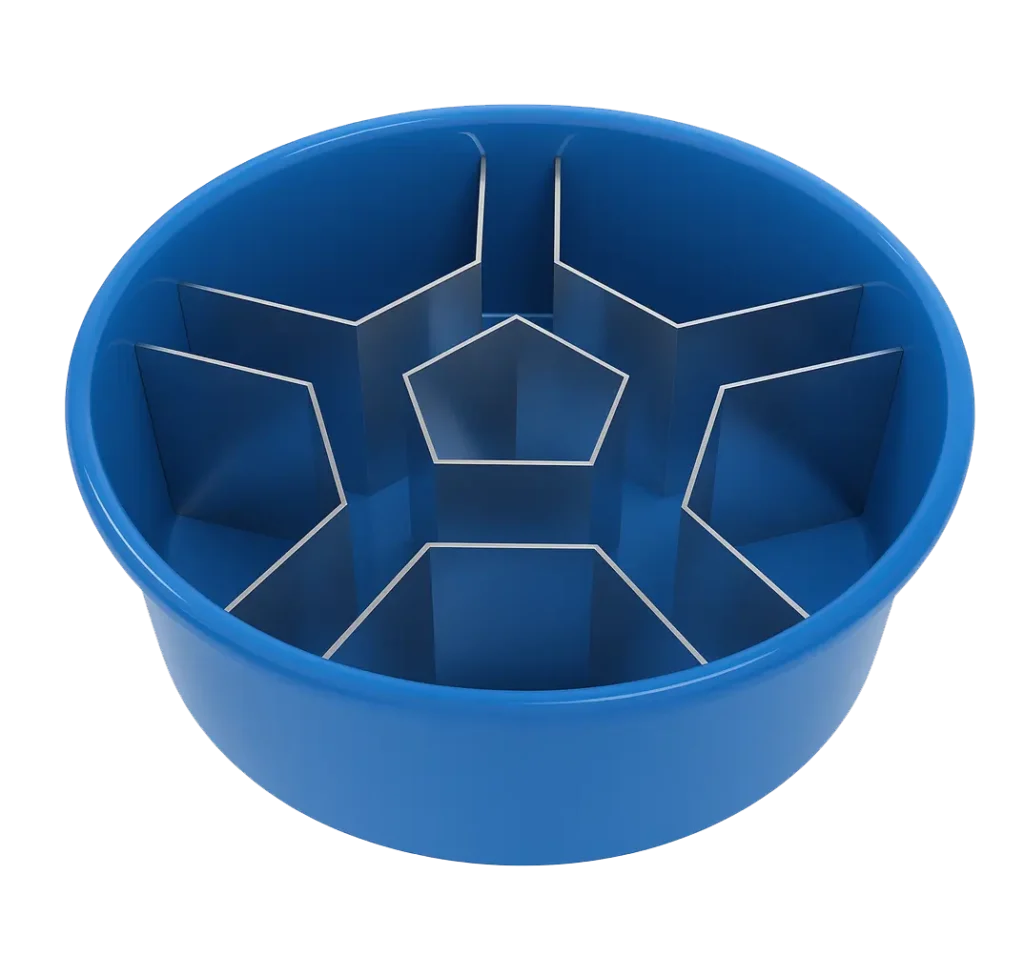

Overview
The Rondi Reig Star Maze was developed by Dr. Laure Rondi-Reig as a tool to study spatial navigation strategies in rodents. By combining features of the Morris Water Maze and T-Maze, the Star Maze enables detailed analysis of navigation processes, distinguishing between allocentric (map-based) and egocentric (route-based) strategies.
Rodents are trained to locate a hidden platform placed within one of the maze’s alleys. By varying the starting points, researchers can observe whether animals rely on external spatial cues, intra-maze cues, or motor sequence memory to solve the task.
Market Opportunity
The Rondi Reig Star Maze expands beyond conventional mazes by:
-
Allowing simultaneous observation of multiple navigation strategies.
-
Providing insights into hippocampal and cerebellar involvement in spatial memory.
-
Offering a translational tool for research into age-related cognitive decline and memory disorders.
-
Combining the strengths of two validated paradigms (Morris Water Maze + T-Maze).
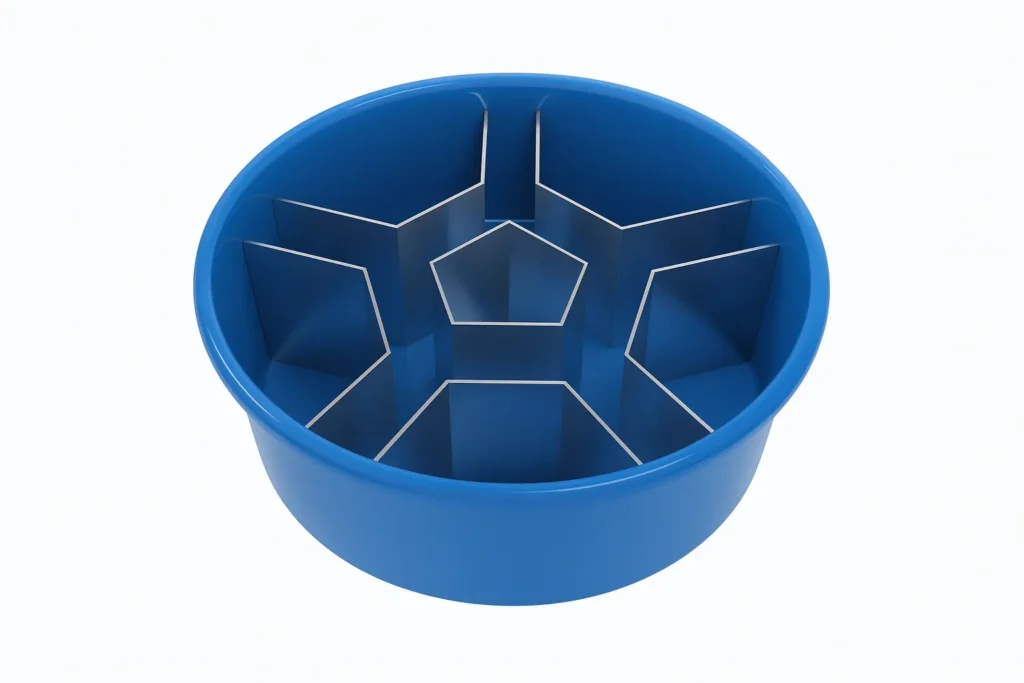

Invention & Advantages

Five-arm star design
Combines a central pentagonal ring with radiating alleys.
Multiple navigation strategies
Differentiates allocentric, sequential-guidance, and egocentric navigation.

Versatility
Can be adapted with intra-maze or distal extra-maze cues.

Dual use
Inserts fit within a Morris Water Maze, enabling both tasks in the same apparatus.
Pharmacological and disease modeling
Stainless steel star insert minimizes corrosion.
Applications
Behavioral Parameters
Time spent mobile vs. freezing (Day 1 and Day 2).
Latency to first head poke.
Number and total time of head pokes.
Shifts in behavior across days (anxiety → exploration).
Use Cases
Study of exploratory drive, anxiety-like behavior, and inhibitory control.
Evaluation of pharmacological interventions.
Developmental and strain-specific behavioral comparisons.
Assessment of GABAergic system functions.
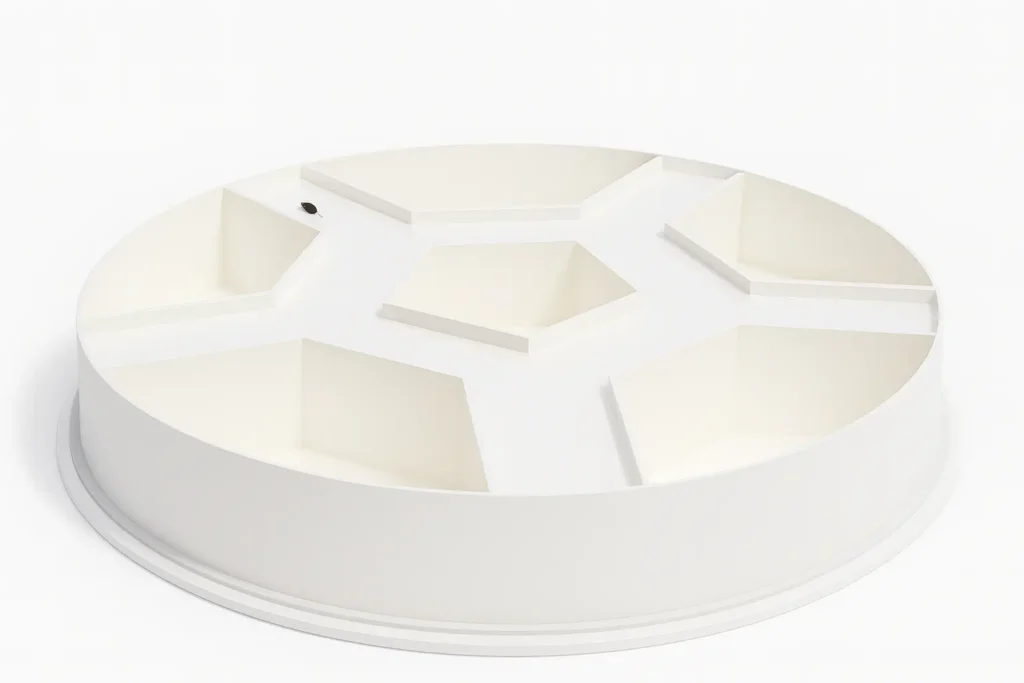

Apparatus & Equipment
- Structure: Five alleys forming an inner pentagon with one alley radiating from each vertex.
- Materials: Stainless steel star insert, aluminum alleys, water-filled tub (4–6 ft diameter).
- Water: Made opaque with non-toxic agents (e.g., powdered milk).
- Platform: Hidden escape platform placed in one alley.
Price & Dimensions
- 4 ft setup: $2,490
- 6 ft setup: $3,290
Training Protocol
- Pre-training:
-
Rodents start from a fixed alley (e.g., Alley 1) to locate a hidden escape platform (e.g., Alley 7).
-
Probe Tests: Starting points are shifted (e.g., Alley 5) to determine navigation strategies.
- Navigation Strategies:
-
Allocentric (map-based) – Uses external cues (room landmarks).
-
Sequential-guidance – Follows a sequence of intra-maze cues.
-
Sequential egocentric – Relies on body turn sequences (left, right, left).
- Variations
-
Allocentric version: Randomized starting points, distal cues visible.
-
Sequential strategies: Black curtain removes external cues, intra-maze patterns used.
Sample Data
-
Mean number of alleys visited can distinguish memory impairments.
-
Knock-out mice show higher alley visits, indicating impaired spatial mapping.
-
Allocentric vs egocentric route use can be compared across groups.

Literature Review
Rondi-Reig et al. (2005): Introduced Star Maze as a paradigm to study multiple navigation strategies.
Rondi-Reig et al. (2006): Showed impairments in allocentric/egocentric strategies in NMDA receptor KO mice.
Morris (1984): Established Morris Water Maze, foundational for Star Maze development.
Packard & McGaugh (1996): Demonstrated hippocampal vs caudate nucleus contributions to navigation.
Principal Investigator
Dr. Laure Rondi-Reig

Professor, Sorbonne University
Neuroscience Department
Head of “Cerebellum, Navigation and Memory” (CeZaMe) Lab
CNRS Bronze Medal (2010),
FRM Iagonitzer Prize (2012),
SATT Lutech Innovation Prize (2019)
References
Morris, R. (1984). Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods, 11(1), 47-60.
Rondi-Reig, L., Petit, G. H., Tobin, C., Tonegawa, S., Mariani, J., & Berthoz, A. (2006). Impaired sequential egocentric and allocentric memories in NMDA receptor KO mice during Star Maze task. J Neurosci, 26(15), 4071-4081.
Rondi-Reig, L., Petit, G., Arleo, A., & Burguière, E. (2005). The Star Maze: a new paradigm to characterize multiple spatial navigation strategies. Behav Res Methods.
Packard MG, McGaugh JL. (1996). Inactivation of hippocampus or caudate nucleus differentially affects place and response learning. Neurobiol Learn Mem, 65:65–72.

Interested in bringing your innovation to life?
Our Tech Transfer program partners with scientists to commercialize cutting-edge neuroscience tools. If you’re an inventor or would like more information on any of the mazes, we’d love to hear from you
