Check our free demo by clicking on the button below
DEMO
| Specifications |
| 3.5 × 3.5 m space |
| Tracked boundary by 30 cm |
| Alarm and visual warning if the user moves beyond the boundary. |
| “‘L’-shaped outward path to three different locations |
| Each marked by inverted cones at head height numbered one two and three |
Parameters to measure
- Time taken to complete the task (seconds)
- Distance travelled (m)
- Time taken to travel to cone 2 (seconds)
- Distance travelled to cone 2 (m)
- Path taken to cone 2
- Time taken to travel to cone 3 (seconds)
- Distance travelled to cone 3 (m)
- Path taken to cone 3
- Time taken to travel back to cone 1 (seconds)
- Distance travelled back to cone 1 (m)
- Path taken back to cone 1
- Speed (m/s)
- Number of ‘out of border’ boundary events (N)
- Length of time in ‘out of border’ boundary (s)
- Distance in ‘out of border’ boundary (m)
- Absolute distance error from location 1 upon return (m)
Protocols
9 trials conducted within each of the three environments, totalling, 27 trials per participant.
Path integration
The return path conditions were altered to three different environments: condition A, no environmental change (Fig. 1D), condition B, removal of boundary cues (Fig. 1E); and condition C, removal of surface detail (Fig. 1F).
Each return condition was presented three times per environment, with return conditions presented pseudo-randomly in each environment.
20 seconds of habituation


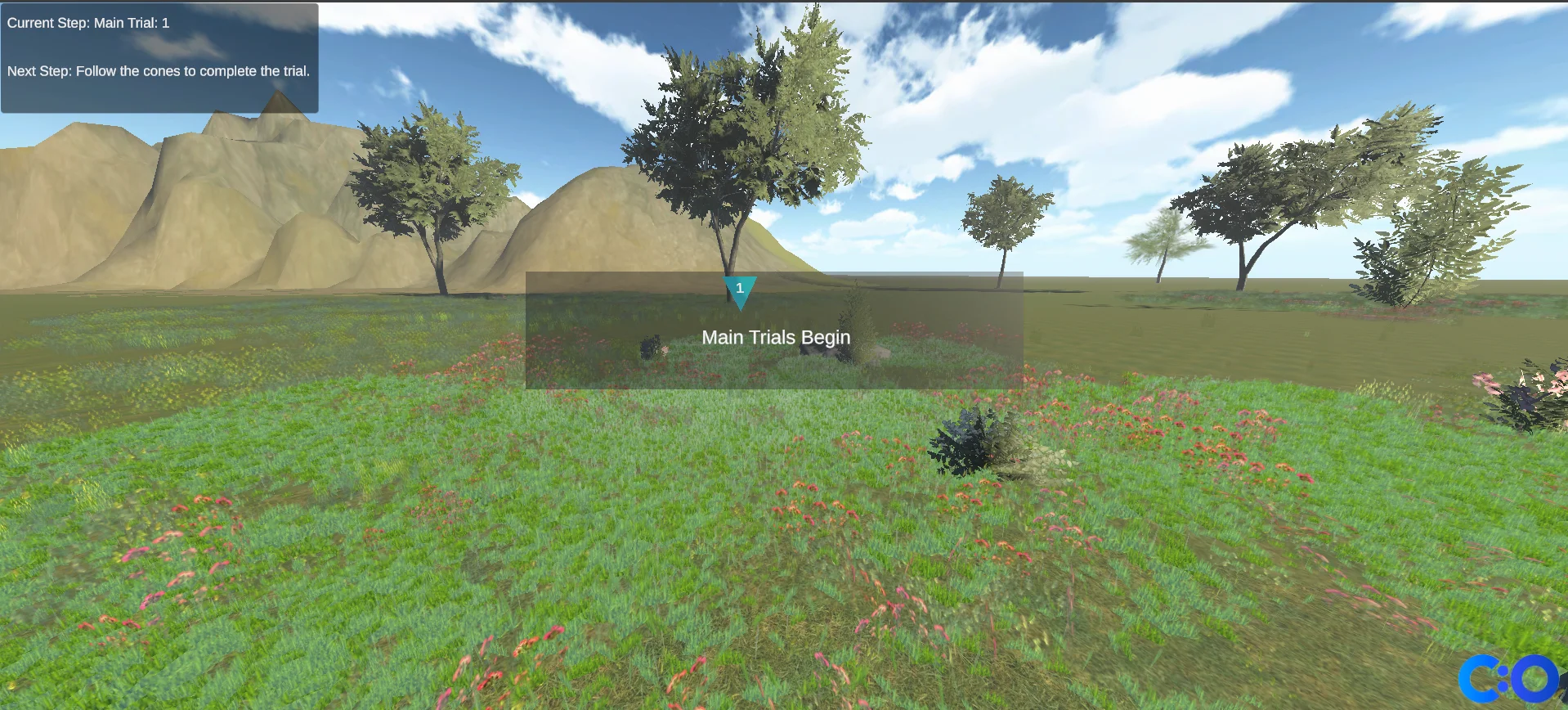
The user is asked to walk in an ‘L’-shaped outward path to three different locations. Inverted cones 2 and 3 disappear once the user reaches them.
Upon reaching cone 3, a message is projected onto the scene asking the user to talk back to location 1 using their memory via a round-trip path.

An auditory stimulus and the appearance of a cone alert participants to walk to the next cone location.
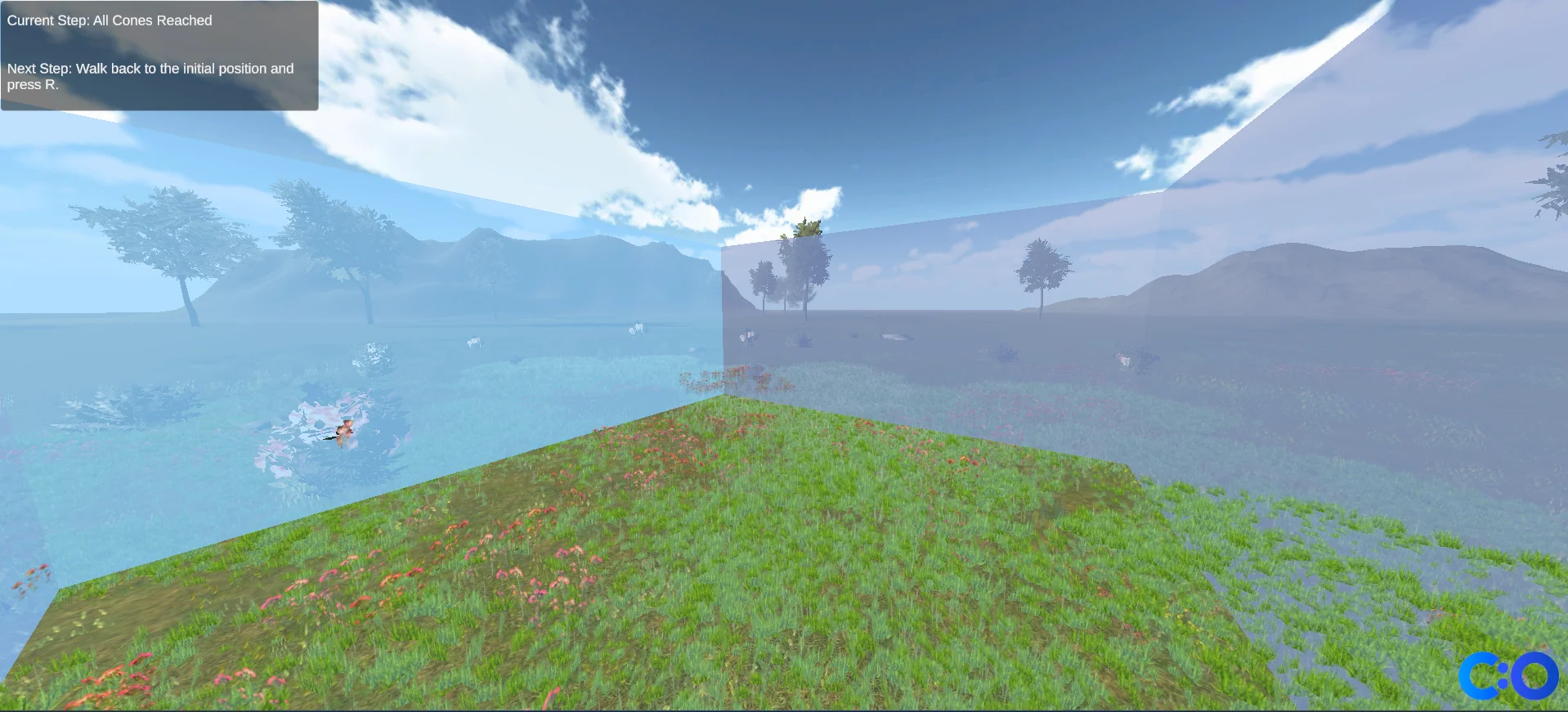
The user presses the controller trigger when he believes he has reached the estimated location of cone 1, which ends the test.
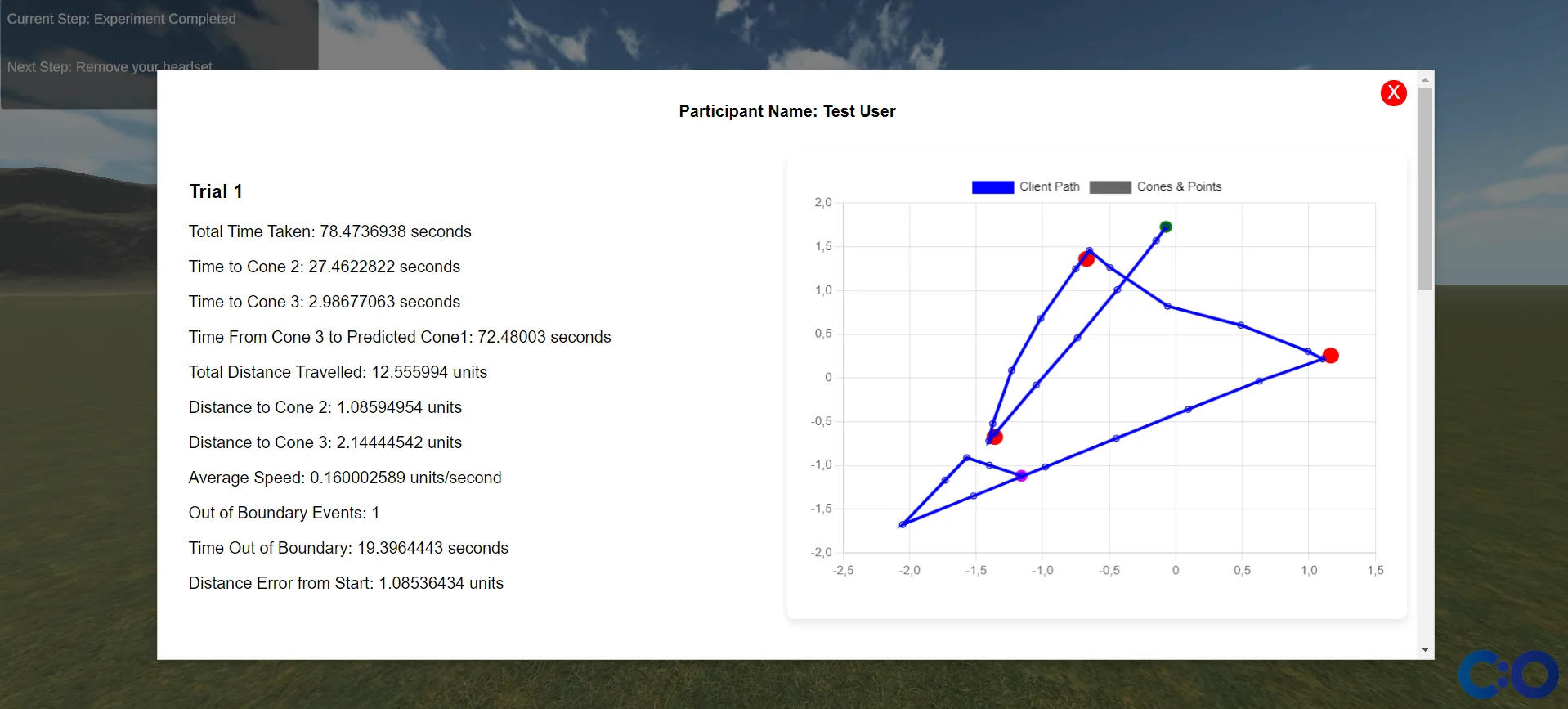
And at the end, the following results are obtained:
References
Vr version:
Howett, D., Castegnaro, A., Krzywicka, K., Hagman, J., Marchment, D., Henson, R., Rio, M., King, J. A., Burgess, N., & Chan, D. (2019). Differentiation of mild cognitive impairment using an entorhinal cortex-based test of virtual reality navigation. Brain, 142(6), 1751-1766.
https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awz116


 The user is asked to walk in an ‘L’-shaped outward path to three different locations. Inverted cones 2 and 3 disappear once the user reaches them.
The user is asked to walk in an ‘L’-shaped outward path to three different locations. Inverted cones 2 and 3 disappear once the user reaches them.
 Upon reaching cone 3, a message is projected onto the scene asking the user to talk back to location 1 using their memory via a round-trip path.
Upon reaching cone 3, a message is projected onto the scene asking the user to talk back to location 1 using their memory via a round-trip path.
 An auditory stimulus and the appearance of a cone alert participants to walk to the next cone location.
An auditory stimulus and the appearance of a cone alert participants to walk to the next cone location.
 The user presses the controller trigger when he believes he has reached the estimated location of cone 1, which ends the test.
And at the end, the following results are obtained:
The user presses the controller trigger when he believes he has reached the estimated location of cone 1, which ends the test.
And at the end, the following results are obtained:

