
Microtome is an instrument used in biological labs to cut thin slices or sections of different materials.[1] There are several types available, and the rotary microtome is one among them.
The rotary microtome cuts the sections when the tissue blocks are moved in a rotary motion using a handwheel.[1] It’s most commonly used for routine research works involving section cuttings from different specimens.
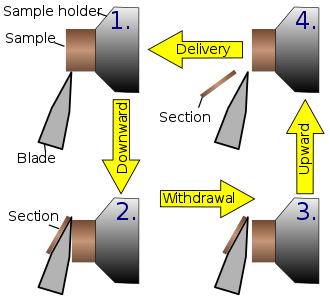
Figure: An illustration of the principle of sample movement in the rotary microtome.[1]
Commercially available microtomes come in three forms: manual, semi-automotive, and automotive. The automated microtome machines have digital keys that control the speed of cutting specimens at your fingertips. It dramatically reduces the stress on your joints.
One similarity between the designs is that they are heavy, weighing about 40 to 60 pounds.[2] It’s mainly to provide stability while cutting the sections of specimens and reduce generated vibrations during the process.[2]
The advantages of rotary microtome include:[2]
This article covers different parts of a rotary microtome, their functions, and factors you need to consider before buying one for your lab.
The rotary microtome consists of the following parts:[3]
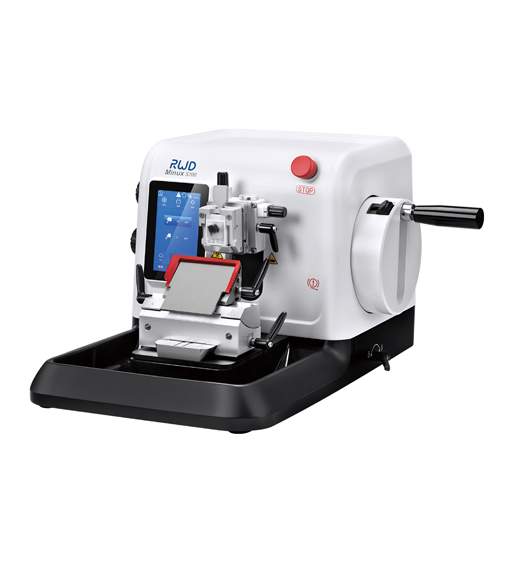

Figure: An image of an advanced high-tech rotary microtome.[4]
A variety of rotary microtomes are available for purchase; thus, getting the right rotary microtome for your lab workflows can be quite confusing. Here are some tips and factors[5] to look over while purchasing a rotary microtome:
It is vital to ensure the quality of the sections when working on a research project or diagnosing a disease. A quality section means precision and stability of tissues and quality of different components of microtome, such as [5]
When the specimen is orientated precisely with a zero-point reference, the block can be aligned quickly and re-cut as needed. Moreover, the electric cooling specimen device in microtomes helps you to obtain uniform sections.[5] However, this feature is optional and isn’t present in all rotary microtomes.
When purchasing a microtome, safety should always be the most important consideration. When working with microtomes, you are close to sharp blades and at risk of cutting yourself.
Many accidents have been reported where lab personnel cut themselves while sectioning specimens, cleaning the machine, removing the blade, or exchanging blocks. [5]
That’s why its necessary to look for the following safety features when buying a rotary microtome:[5]
Although manual machines are less expensive than automated ones, automated rotary microtomes have many advantages in terms of ergonomics and safety features:[5]
Here are some questions to ask yourself before choosing a brand:
Research the brand and see how long it has been in the industry, what its customers say about their buying experience, and if the company offers a high level of customer service, ranging from sales, delivery, and installation, to sales support.
Consult your peers whom you know working with a similar kind of lab workflow like yours or who have worked with microtomes. Ask them about their experience with the machine, visited shops/places, reliable options, and feature selection.
See if they have qualified engineers for maintenance and repair processes. Also, check the warranty duration provided by the brands and if the supplier has the necessary parts of the equipment in their original forms.
Additionally, consider your budget, applications you need to perform, blade material, required section thickness, and type of knife (fixed or disposable) required for your lab procedures.
Related Read: Tips and Factors To Consider When Buying a Microtome
A rotary microtome is a precision tool used to cut sections with thicknesses ranging from 1 micron to 60 microns of a variety of specimens for a range of lab workflows.
It has a static knife and the object block moves in an up-and-down motion while spinning the handwheel to obtain the section.
The broad variety of rotary microtomes available makes it difficult to choose the right one for your lab. However, factors like the quality of sections obtainable, in-built safety features, budget, brand reputation, and materials used to build the instrument, should ultimately decide the exact product you go for.
Check out our S700A rotary microtome if you want an easy-to-operate, easy-to-clean microtome with high-end safety and technical features.

Monday – Friday
9 AM – 5 PM EST
DISCLAIMER: ConductScience and affiliate products are NOT designed for human consumption, testing, or clinical utilization. They are designed for pre-clinical utilization only. Customers purchasing apparatus for the purposes of scientific research or veterinary care affirm adherence to applicable regulatory bodies for the country in which their research or care is conducted.