$0.00
The Semi-Auto Microtomes are designed for efficient and precise sectioning in histology and pathology. These instruments offer a blend of manual control and automated assistance, making them suitable for a variety of laboratory needs.
The RF-RD-485 provides consistent performance for routine sectioning tasks. For enhanced capabilities, the RF-RD-485Pro includes additional features such as automated tool alignment, remote operation, and cut counting. Both models facilitate the preparation of accurate, reproducible tissue sections for microscopic analysis.
ConductScience offers the Semi-Auto Microtome Solutions

ConductScience is a company specializing in providing high-quality research equipment, lab supplies, and scientific services for the life sciences community.



Model | Semi-auto RF-RD-485 | Semi-auto PRO RF-RD-485PRO |
|---|---|---|
Section thickness setting range: | 0-99.9µm increment: 0.1µm | |
Trimming thickness setting range: | 0-999µm increment: 0.1µm | |
Specimen retraction: | 0-100µm(can close) | |
Precision and error: | ±1% | |
Fast feed speed adjust: | 1mm/s ~3.5mm/s, at any set | |
Maximum specimen size: | 60mmx50mm | |
Maximum specimen size: | 28mm | |
Specimen vertical feeding: | 60mm | |
Slow feed speed adjust: | 0.1mm/s ~1mm/s, at any set | |
Specimen clamp rotation: | At any angle within 360° | |
Specimen orientation system | XY -15° | |
Net weight: | 35KG | |
Size: | 580mm*490mm*315mm(L*W*H) | |
Specimen clamp: | Paraffin block clamp or cassette clamp , optional | |
Blade holder: | In high or in low profile blade holder, optional | |
Voltage and frequency: | AC220V±10% 50Hz(standard model);AC110V±10% 60Hz |
Robust and Easy-to-Clean Design: Features an easy-to-clean housing and a sturdy base for stability. Includes a wide, removable waste tray.
Dual Handwheel Locking System: Offers two independent locking positions: at any 360° position and a quick lock at the top end.
Optimized Sample Feed: Provides continuous action from 0.1mm/s to 3.5mm/s and single-point action from 1µm to 100µm for sample forward and backward movement.
High-Definition Color Touch Screen: Displays all essential parameters like section mode, thickness, section counter, and retraction. Equipped with a high-precision controller and photoelectric sensing system for 0.1µm slicing accuracy.
Automatic Tool Alignment: Tissue automatically moves to the blade edge when activated, streamlining setup.
External Remote Control: Operate all functions conveniently via the included remote control.
Intelligent Slice Counting: Accurately records slicing data by automatically excluding trimming values.
Half-Cycle Reciprocal Mode: Features a specialized slicing/trimming mode for enhanced efficiency.
Configurable Sleep Mode: The machine can automatically enter a customizable sleep mode to save energy.
Triple Handwheel Locking: Enjoy three independent locking options: any 360° position, a quick top-end lock, and an electronic lock.
Adjustable Specimen Clamp: Offers 16° horizontal and vertical adjustment, plus 360° rotation for easy sample positioning during trimming.
One-Button Return: Quickly replace specimens with a simple press of a button.
Real-time Specimen Position Display: Monitor the clamp’s position in real time, complete with limit alarms.
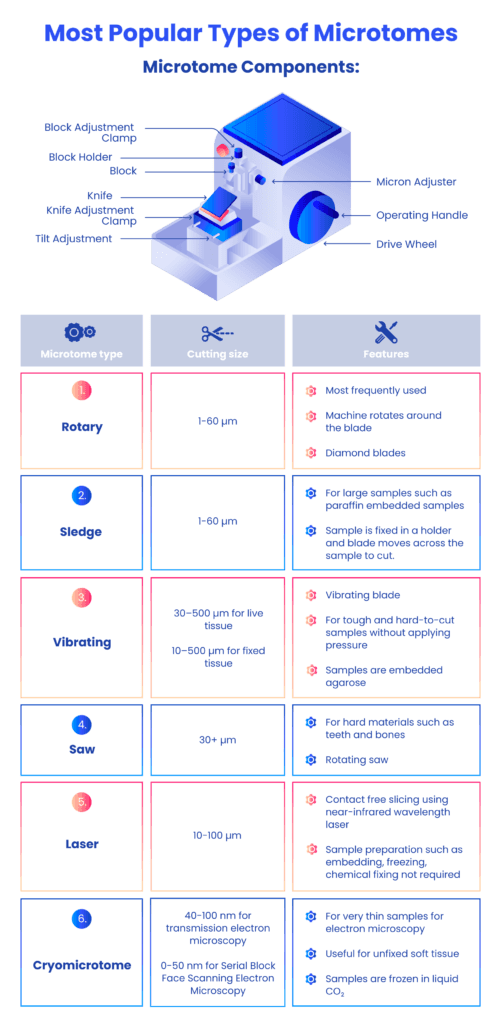
A Rotary microtome cuts the sections of biological specimens into thin slices for use in microscopy. It gets its name because of the rotary action of the handwheel used for slicing samples. It is used to prepare thin layers of bone, mineral, teeth, and hair with section thicknesses ranging from 1-micron to 60 microns. For hard materials that use synthetic resins, they can slice up to 0.5 microns.
The knife holder base holds the holder in place on the microtome stage. It can be moved to or away from the block, but it must remain fixed and secured during microtomy.
The knife holder comprises various parts, including the blade clamp, which holds the blade, the knife tilt, which adjusts the knife angle, and the faceplate, which directs the ribbons away from the blade and toward the operator.
The microtome body is a platform with rails that keeps the knife holder base in place.
The block holder or cassette clamp holds the paraffin block in place. The block usually slides up and down with each revolution while the blade remains stationary. The block holder may be equipped with knobs that enable the operator to move the block face in different directions to line the tissue with the blade.
The advancement handwheel rotates in one direction, moving the block closer to the knife at the preset microns.
The coarse handwheel moves the block closer or away from the knife.
Micron adjustment is used to adjust settings for slice thickness that vary from 1 to 60 microns.
The handwheel includes a safety lock that prevents the wheel from loosening and the block holder from falling towards the blade when inserting or removing a block.
The Rotary microtome uses a staged rotary action where the specimen is cut with the circular motion of the handwheel. The cutting procedure is done with a knife or disposable blade placed within the instrument.
The Rotary microtome is used to cut biological specimens according to the desired thickness ranging from 1 to 60 microns. It may be adapted to various types of tissue sectioning (hard, brittle, or fatty). However, it is not suitable for large tissue sectioning. Technological advancements in the rotary microtome have enhanced section quality, boosted production, and improved the technologist’s occupational safety.
The incidence of repetitive motion disorders, a frequent occupational health concern in the histology laboratory, may be reduced by eliminating the manual hand-wheel operation of the microtome. Disposable blades are used, eliminating the need for sharpening and increasing sample size accuracy. Additionally, knives can be used in place of blades; they are thick and large and produce fewer vibrations during microtomy. A high-resolution motor makes a stable and smooth automatic slicing system. Its heavier size makes it stable, and it is crucial to avoid undulations in the paraffin sections. A double locking system makes it secure and prevents injuries during block handling. An emergency button is used to stop the operation in danger. It is anti-static, non-waxing, and is very easy to clean. It has four different automatic slicing modes that cover a lot of sampling situations. Daily cleaning from paraffin residue maintains a microtome cutting ideally for many years.
The heavy size of the rotary microtome makes it less portable. The disposable blades are expensive and need to be handled with care to avoid accidents. Moreover, the knives get dull if they aren’t used on decalcified tissue that hasn’t been cleaned.
| Weight | 6.61 lbs |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 34 × 25 × 20 cm |
| Model | Standard, PRO Version |
You must be logged in to post a review.
There are no questions yet. Be the first to ask a question about this product.
Monday – Friday
9 AM – 5 PM EST
DISCLAIMER: ConductScience and affiliate products are NOT designed for human consumption, testing, or clinical utilization. They are designed for pre-clinical utilization only. Customers purchasing apparatus for the purposes of scientific research or veterinary care affirm adherence to applicable regulatory bodies for the country in which their research or care is conducted.
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.